Food Carbon Footprint: Diet Emissions Guide & Meal Swaps
Food production creates 26% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Your diet determines your personal footprint. Meat-heavy diets produce approximately 2.5 tons of CO₂ per year; vegetarian diets produce 1.5 tons. Vegan diets are 1 ton. Switching to plant-based foods reduces 1–1.5 tons yearly.
Food Carbon Footprint Types
-
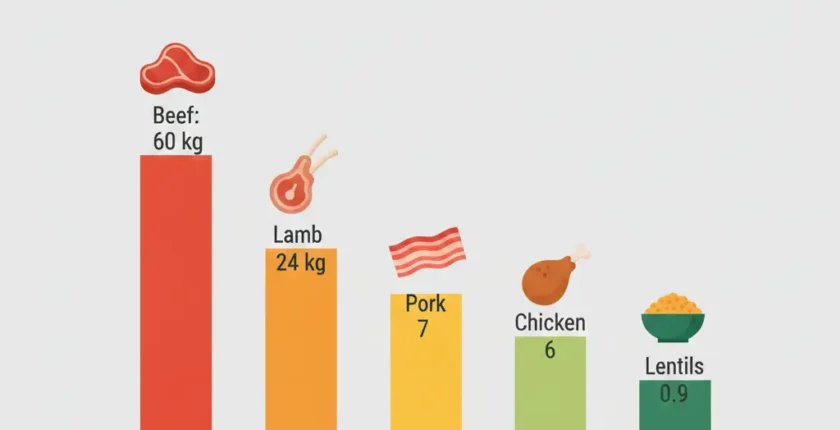
Beef: 60 kg CO₂ per kg. Highland and methane emissions.
-
Lamb: 24 kg CO₂ per kg. Methane from digestion.
-
Pork: 7 kg CO₂ per kg. More efficient feed conversion.
-
Chicken: 6 kg CO₂ per kg. Fast growth, no methane.
-
Dairy: Milk 3 kg, cheese 13 kg CO₂ per kg.
-
Plant foods: Grains < 1 kg, vegetables 2 kg, fruits 1 kg.
Food accounts for 26% of global emissions. Our complete guide to calculating and reducing your carbon footprint shows how diet fits into your total impact.
Diet choices create 20-30% of personal emissions. Calculate your food carbon footprint to see your dietary impact.
Practical Food Changes
-
Swap beef for chicken twice weekly: saves 550 kg CO₂/year.
-
Meatless Monday saves 150 kg CO₂/year.
-
Reduce portions: smaller servings cut emissions proportionally.
-
Choose plant proteins: lentils provide the protein of 3 oz of steak with 95% lower emissions.
-
Limit dairy; oat milk produces 80% fewer emissions than cow milk.
-
Reduce food waste: prevents emissions from production and landfill methane.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How does meat consumption affect carbon footprint?
Red meat has the highest emissions. Learn how to measure your complete carbon footprint to see your diet’s impact.
Q: Are local foods better for carbon emissions?
Transportation is a small fraction. Production type matters more.
Q: Does food waste contribute to the carbon footprint?
Yes. Wasted food emits CO₂ during production and methane when decomposed.
Q: Which plant foods have the lowest emissions?
Grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables generally produce minimal CO₂.
Track how your food choices affect the planet. Get personalized meal swap recommendations.